Giải tiếng Anh lớp 12 Unit 16: THE ASSOCIATION OF SOUTHEAST ASIAN NATIONS
5Kẫ
THE ASSOCIATION OF SOUTHEAST ASIAN NATIONS
(Hiệp hội các quốc gia Đông Nam Ả)
I. VOCABULARY
original
[s’nd^inl]
(adj)
đầu tiên, nguyên gốc
origin
[‘Drid3in]
(n)
gốc, khởi nguyên
namely
[neimli]
(adv)
cụ thể là, ấy là
accelerate
[ok’selareit]
(V)
thúc đẩy, đẩy nhanh
acceleration
[akselo’reijn]
(n)
sự làm nhanh thêm
accelerator
[ok’selareito]
(n)
người/vật làm tăng tốc
accelerative
[ok’selaretiv]
(adj)
làm nhanh thêm
stability
[sta’bibti]
(n)
sự bền vững/ổn định
stable
i'steibl]
(adj)
ổn định
account for
[o’kuont fa]
(V)
giải thích, chiếm
diverse
[dai’v3:s]
(adj)
đa dạng, nhiều loại khác nhau
diversity
[dai’v3:s3ti]
(n)
tình trạng đa dạng
diversify
[dai’v3:sifai]
(V)
làm thành đa dạng
GDP [cfci:di:’pi:]: Gross Domestic Product (phr)
tổng giá trị hàng hóa và dịch vụ,
adoption
[o’dDpfn]
(n)
sản xuất trong nước trong một năm formally approval: sự chính thức
adopt
[o’dDpt]
(V)
chấp/thừa nhận chấp nhận
vision
[‘vi3n]
(n)
tầm nhìn, viễn tưởng
forge
[fo:d3]
(V)
form: tạo dựng
integration
[into’greijn]
(n)
sự hội nhập/hòa nhập
integrate
[‘intogreit]
(V)
hợp nhất
integrated
[‘intogreitid]
(adj)
hòa hợp, hòa nhập
realization
[riolai’zeijn]
(n)
sự thực hiện, hiện thực hóa
realize
[‘riolaiz]
(V)
compliment: thực hiện
realizable
[‘riolaizobl]
(adj)
achieve: đạt được
achievable: khả thi, có thể thực hiện
rural
[‘rosrl]
(adj)
thuộc về nông thôn
urban
[l3:bn]
(adj)
thuộc về thành phô'
rural development enterprise
[‘entaprais]
(n)
(n)
phát triển nông thôn doanh nghiệp
medium enterprise
[‘mkdiom]
(n)
doanh nghiệp vừa
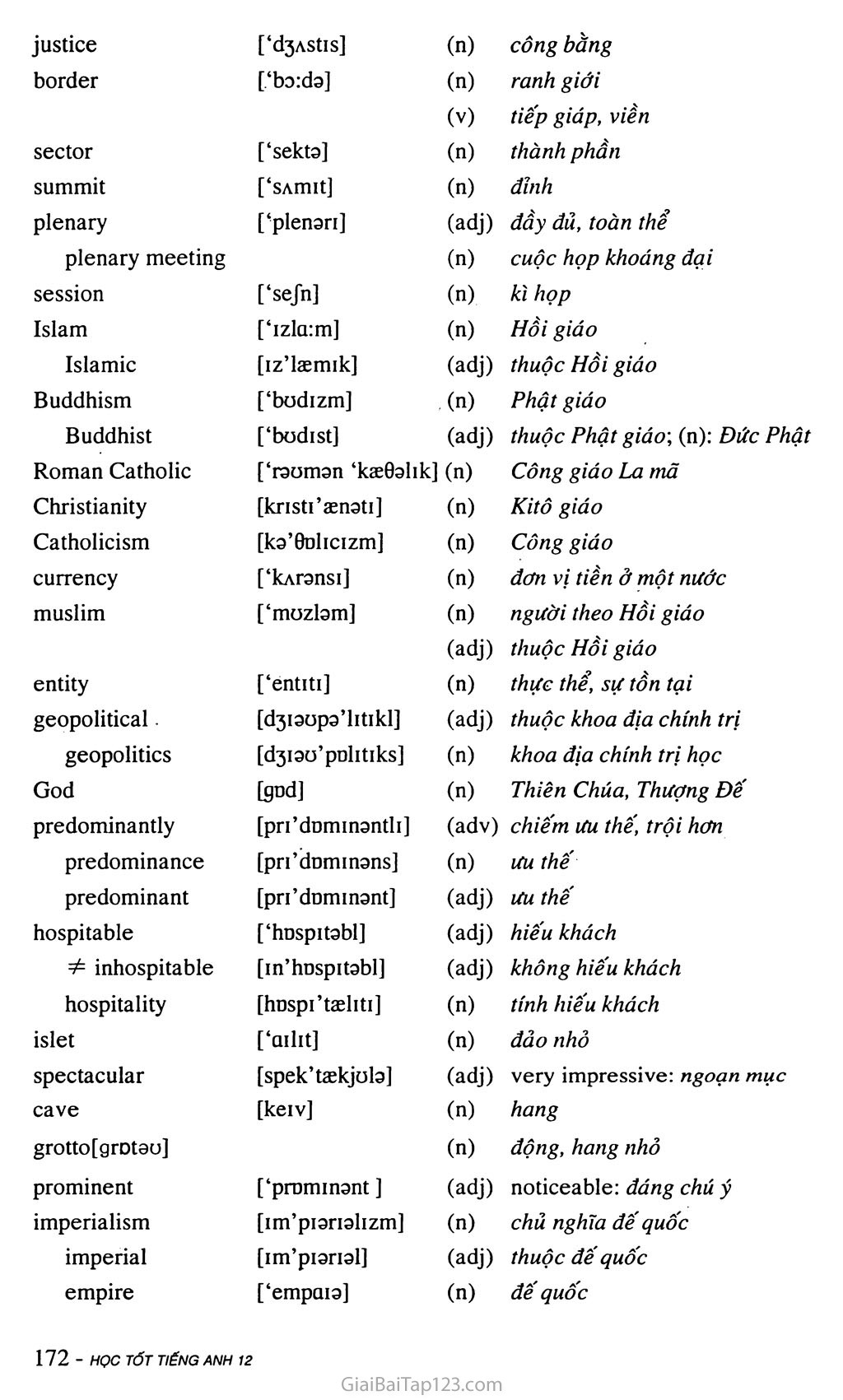
justice
[ld3AStis]
(n)
công bằng
border
[,‘ba:da]
(n)
(V)
ranh giới tiếp giáp, viền
sector
[‘sekta]
(n)
thành phần
summit
[‘sAmit]
(n)
đỉnh
plenary
[■plenari]
(adj)
đầy đủ, toàn thể
plenary meeting
(n)
cuộc họp khoáng đại
session
[‘sejn]
(n)
kì họp
Islam
[‘izla:m]
(n)
Hồi giáo
Islamic
[iz’kemik]
(adj)
thuộc Hồi giáo
Buddhism
[‘bodizm]
(n)
Phật giáo
Buddhist
[‘bodist]
(adj)
thuộc Phật giáo; (n): Đức Phật
Roman Catholic
[‘raoman ‘kaeOalik] (n)
Công giáo La mã
Christianity
[kristi’asnati]
(n)
Kitô giáo
Catholicism
[ka’0Dlicizm]
(n)
Công giáo
currency
[‘kAransi]
(n)
đơn vị tiền ở một nước
muslim
[‘mozlam]
(n)
(adj)
người theo Hồi giáo thuộc Hồi giáo
entity
[‘entiti]
(n)
thực thể, sự tồn tại
geopolitical
[d3iaopa’litikl]
(adj)
thuộc khoa địa chính trị
geopolitics
[d3iao’pnlitiks]
(n)
khoa địa chính trị học
God
[gnd]
(n)
Thiên Chúa, Thượng Đế
predominantly
[pri’dDminantli]
(adv) chiếm ưu thế, trội hơn
predominance
[pri’dDminans]
(n)
ưu thê'
predominant
[predominant]
(adj)
ưu thế
hospitable
[‘hDspitabl]
(adj)
hiếu khách
#= inhospitable
[in’hDspitabl]
(adj)
không hiếu khách
hospitality
[hDspi’tseliti]
(n)
tính hiếu khách
islet
[‘ailit]
(n)
đảo nhỏ
spectacular
[spek’taskjola]
(adj)
very impressive: ngoạn mục
cave
[keiv]
(n)
hang
grotto [grDtau]
(n)
động, hang nhỏ
prominent
[‘prominant ]
(adj)
noticeable: đáng chú ý
imperialism
[im’piarializm]
(n)
chủ nghĩa đê' quốc
imperial
[im’piarial]
(adj)
thuộc đế quốc
empire
[‘empaia]
(n)
đê' quốc
emperor [‘empore] (n) hoàng đế
II. GRAMMAR
ADVERB CLAUSES of TIME
(Mệnh đề trạng từ chỉ thời gian)
Liên từ (Conjunctions) Mệnh đề trạng từ chỉ thời gian thường được giới thiệu bởi những liên từ như: when, before, after, as, while, since, until, as soon as, every time (that), the moment (that), the minute (that), as/so long as (bao lâu), just as, just after,...
Dạng động từ ở mệnh đề thời gian (Verb forms of Time clauses).
Thì Tương lai (Future tenses) không được dùng ở mệnh đề chỉ thời gian ở tương lai.
Thì Tương lai đơn (Simple future): được thay bằng Thì Hiện tại đơn (Simple present).
e.g.: He’ll come back . I’ll wait here. (Anh ấy sẽ trở lại. Tôi sẽ chờ ở đây.)
=> I’ll wait here until he comes back.
Thì Hiện tại điều kiện (Present conditional tense) được thay bằng thì Quá khứ đơn (Simple past).
e.g.: We knew he would arrive. Nothing could be done then.
(Chúng tôi biết anh ấy sẽ đến. Không gì được làm cho đến lúc đó.)
=> We knew nothing could be done until he arrived.
Thì Tương lai hoàn thành (Simple future perfect) được thay bằng í/zỉ Hiện tại hoàn thành (the Simple present perfect). .
e.g.: He will go home. He will have closed the shop before then.
(Anh ấy sẽ về nhà. Anh ấy sẽ đóng cửa tiệm trước đó.)
=> He will go home after he has closed the shop.
Những từ: AFTER, BEFORE, WHEN, SINCE có thể được theo sau bởi danh động từ (gerund).
e.g.: After doing exercise, he usually has a hot bath.
(Sau khi tập thể dục, ông ấy thường tắm nước nóng.)
Phân từ - Hiện tại hay Quá khứ - có thể dùng sau những liên từ: WHEN,
UNTIL, WHILE, ONCE,...
e.g.: Please wait until told to do. (Vui lòng chờ cho đến khi được bảo làm.)
=> Please wait until you are told to do.
Take care when crossing the streets. (Hãy cẩn thận khi băng qua đường phố.) => Take care when you are crossing the streets.
WHILE - AS: chỉ sự kiện diễn tiến trong một khoảng thời gian ngắn, và thường đi với Thì Tiếp diễn (Continuous tenses).
e.g.: As we were walking through the wood, we saw a fox.
(Trong khi đi ngang qua khu rừng, chúng tôi thấy một con chồn.)
Đê’ nhấn mạnh sự kiện xảy ra ngay sau sự kiện khác, chúng ta dùng JUST AFTERJAS, IMMEDIATELY, THE MINUTE (that), THE MOMENT (that), ..
e.g.: Just as/after you get the letter, let me know.
(Cho tôi biết ngay khi bạn nhận lá thư.)
SINCE + mệnh đề với động tù ở
Thì Quá khứ đơn, mệnh đề chính ở Thì Hiện tại hoàn thành (đơn/tiếp diễn), e.g.: Since he was a child, he has done hard work.
(Từ khi còn là cậu bé, nó đã làm công việc nặng nhọc.)
Thì Hiện tại hoàn thành (đơn/tiếp diễn): nhân mạnh sự kiện còn tiếp tục ở hiện tại.
e.g.: Since he has lived/has been living in this city, he has been selling the lottery. (Ong ấy bán vé số từ khi sống ở thành phô' này.)
III. SOLUTIONS and TRANSLATIONS (Lời giải và Bài dịch)
A. READING
Before You Read
Work in pairs. Ask and answer the following questions. (Làm việc từng đôi. Hỏi và trả lời các câu hỏi sau.)
It stands for Association of South East Asian Nations.
Vietnam joined this association in 1995.
While You Read
Read the passage and do the tasks that follow. (Đọc đoạn văn và làm bài tập kèm theo.)
Hiệp Hội các quốc gia Đông Nam Á, hay ASEAN, được thành lập ngày 8 tháng 8, 1967, ở Bangkok, Thái Lan bởi năm nước thành viên đầu tiên, đó là: In-đô-nê- zia, Mã Lai, Phi Luật Tân, Sin-ơ-pho và Thái Lan. Bru-nê gia nhập ASEAN năm 1984. Việt Nam trở thành thành viên thứ bảy năm 1995. Lào và Myanmar được nhận vào Hiệp hội này năm 1997, và Cam-pu-chia năm .1999. Mục tiêu chính của Hiệp hội là đẩy mạnh phát triền kinh tế, tiến bộ xã hội và phát triển văn hóa; và thăng tiến hòa bình và sự bền vững qua sự tôn trọng công bằng, và quy tắc luật pháp trong mốì quan hệ giữa các quốc gia trong vùng.
ASEAN có dân sô' là 575,5 triệu người, chiếm khoảng 8,7% dân sô' thê' giới. Tổng diện tích là 4.454.322 cây sô' vuông. Nó là một vùng văn hóa đa dạng, và ở một vài quốc gia như Phi Luật Tân, Bru-nê, Mã Lai và Sin-ga-po nói tiếng Anh ngoài ngôn ngữ riêng của họ. Theo sô' thông kê ghi năm 2007, ASEAN có GDP hỗn hợp khoảng 1.282 tỉ Mĩ kim (đô-la), Con sô' GDP hỗn hợp này tăng với tỉ lệ trung bình khoảng 6% mỗi năm từ 2003 đến 2007. Nền kinh tê' của các nước thành viên rất đa dạng mặc dù những sản phẩn chính bao gồm hàng điện tử, dầu và gỗ. Chính phủ của ASEAN đặc biệt chú ý đến thương mại. Năm 2006, vùng ASEAN đã đạt tổng sô' thương mại là 1.405 tỉ Mĩ kim. Người ta ước tính rằng khu mậu dịch tự do sẽ
được thiết lập trong vùng trước năm 2020. Các nhà lãnh đạo ASEAN cũng đã chấp thuận Tầm Nhìn ASEAN nhằm thành lập sự hội nhập kinh tế chặt chẽ hơn trong vùng. Kế Hoạch Hành Động Hà Nội, được chấp thuận năm 1998, dùng như hành động đầu tiên của một loạt hành động được hoạch định dẫn đến sự thực hiện Tầm Nhìn ASEAN.
Ngày nay, sự hợp tác kinh tế của ASEAN bao gồm nhiều lãnh vực: thương mại, đầu tư, công nghiệp, dịch vụ, tài chính, nông nghiệp, phát triển nông thôn, lâm nghiệp, năng lương, vận tải và giao thông, khoa học và kĩ thuật, doanh nghiệp nhỏ và vừa, và du lịch. ASEAN đã hoạt động tích cực để cải tiến tình hình kinh tế xã hội và giải quyết các khó khăn giữa các quốc gia thành viên.
Task 1 : The words in the box all appear in the passage. Fill in each blank with a suitable word. {Tất cả những từ trong khung xuất hiện ở đoạn văn. Điền mỗi chỗ trống với từ thích hợp.)
justice 2. GDP 3. diverse
4. integration 5. accelerate 6. enterprises
Task 2: Decide whether the following statements are true (T) or false (F). {Quyết định những câu sau đúng (T) hay sai (F))
T 2.F 3.F 4.T 5.F 6.F
Task 3: Answer the following questions. {Trả lời các câu hỏi sau.)
Five original countries, namely Indonesia, Malaysia, the Philippines, Singapore and Thailand, founded ASEAN.
The two main goals of the Association are to accelerate the economic growth, social progress and cultural development and to promote peace and stability through respect for justice and the rule of law in the relationship among countries in the region.
ItwasUSS 1405 billion.
It was adopted in 1998.
It includes many areas: trade, investment, industry, services, finance, agriculture, rural development, forestry, energy, transportation and communication, science and technology, small and medium enterprises, and tourism.
❖ After You Read
Work in groups. Summarize the passage, based on the years: 1967, 1995, 1997, 1998, 1999, 2007, 2020.
(Possible answer)
In 1967, ASEAN was founded in Bangkok, Thailand by the five original countries.
In 1995, Vietnam became the seventh member of the Association,
Laos and Myanmar were admitted to ASEAN in 1997.
D. In 1999, Cambodia joined this Association.
A. In 1998, the Ha Noi Plan of Action was adopted, which aimed to lead up to the realization of the ASEAN Vision.
B. According to the statistics in 2007, ASEAN had a combined GDP of about US $ 1 282 billion.
D. By 2020 a free trade area will have been established in the region of ASEAN.
B. SPEAKING
Task 1: Work in pairs. Discuss and write down the name of the country and its capital under each national flag. {Làm việc từng đôi. Thảo luận và viết tên của quốc gia và thủ đô của nó dưới mỗi quốc kì.)
1. Country: Malaysia -
Capital: Kuala Lumpur
2. Country: The Philippines
Capital: Manila
3. Country: Laos
Capital: Vientiane
4. Country: Singapore
Capital: Singapore
5. Country: Indonesia
Capital: Jakarta
6. Country: Thailand
Capital: Bangkok
7. Country: Myannmar
Capital: Rangoon
8. Country: Cambodia
Capital: Phnom Penh
9. Country: Brunei
Capital: Banda Seri Begawan
Task 2. Work in groups. Discuss and use the information in Task 1 and the facts below to talk about some of the ASEAN countries. {Làm việc từng nhóm. Thảo luận và dùng thông tin ở Task 1 và những sự kiện dưới đây để nói về một vài nước của ASEAN.)
Malaysia has a total area of 329,758 square kilometres. Its capital is Kuala Lumpur. It has a population of 24,014,200 people. The official languages used in Malaysia are Malay, English and Tamil. The main religions in Malaysia are Islam and Buddhism, and its currency unit is Ringgit.
Thailand has a total area of 514,000 square kilometres. Its capital is Bangkok. It has a population of 64,420,000 people. The official language spoken in Thailand is Thai. Buddhism is its national religion. Baht is the local currency unit.
The Philippines are an archipelago of 7,000 islands lying off the southeast of Asia. It has a total area of 300,000 square kilometres. Its capital is Manila. It has a population of 91,077,287 people. The main languages spoken in the Philippines are Filipino and English. The main religion in the Philippines is Roman Catholics. The monetary unit of the Philippines is Peso.
c. LISTENING
❖ Before You Listen
Work in pairs. Ask and answer the following questions: Which ASEAN countries use English as a second language? {Làm việc từng đôi. Hỏi và trả lời câu hỏi: “Những quốc gia nào của ASEAN dùng tiếng Anh như ngôn ngữ thứ hai?)
Which countries of ASEAN use English as a second language?
Some countries of ASEAN, which use English as a second language, are the Philippines, Malaysia, and Brunei.
While You Listen
Task 1: Listen to the dialogue between Mr Hung and his daughter Nga, and choose the best answer A, B, or c to complete each of the following sentences. {Nghe cuộc đối thoại giữa ông Hùng và con gái Nga, và chọn câu trả lời đúng nhất A, B hay c để điền mỗi câu sau.)
l.c 2. A 3. c 4. A 5.B
Tapescript
Mr Hung: What are you doing? It’s so late. Why don’t you go to bed?
Nga: I’m trying to finish my essay about the culture and religion of the ASEAN countries. I’ll have to submit it to my teacher tomorrow. May I ask you something, Dad?
Mr Hung: Yes? What’s that?
Nga: Do you know how many people in the Southeast Asia speak English?
Mr Hung: I’m not sure. But the ASEAN countries have the third largest number of English speakers - just after the US and UK.
Nga: Really? Exactly how many people speak English?
Mr Hung: Around 50 million, I think. - mostly in the Philippines.
Nga: Do you know anything about religions?
Mr Hung : The ASEAN countries include three main religions. They are Islam, Buddhism and Catholicism.
Nga: What is Islam?
Mr Hung : A religion based on a belief in one god and the teaching of Muhammad. It’s the religion of the Muslims.
Nga: Can you tell me something more about the Muslims?
Mr Hung: It’s an interesting question. The ASEAN countries have more Muslims than any other geo-political entity.
Nga: But how many Muslims, Dad?
Mr Hung : Oh, let me try to remember... about a quarter of a billion, mostly in Indonesia and Malaysia.
Nga: And what about the other religions?
Mr Hung : Other main religions of the various countries in the region include large numbers of Buddhists, and the Catholics in the Philippines.
Nga: What is the main religion in Vietnam?
Mr Hung : It’s Buddhism. Many people go to pagoda.
Nga: Well, and now I think I’ve got all the information I need for my essay. Thank you very much, Dad.
Mr Hung : That’s all right. Finish your writing and go to bed. I’m afraid you’ll get up late tomorow morning.
Task 2: Answer the following questions. (Trả lời các câu hỏi sau.)
. 1. She has to submit it to her teacher tomorrow morning.
The US.
It’s around 50 million.
It’s the Philippines.
There are three, and they are Islam, Buddhism and Catholicism.
❖ After You Listen
Work in groups. In your opinion, what do you think Nga’s essay will be about?
A: What do you think Nga’s essay will be about?
B: About the language and religions in the ASEAN countries
C: What religions does she want to know?
D: The main religions in the area are Islam, Buddhism and Catholicism.
A: Does she ask whether English is spoken in the ASEAN countries?
B: Yes. And her father let her know that the ASEAN countries ranks the third where English is spoken.
C: Really? How interesting!
D. WRITING
Task 1: Complete the letter of recommendation with the missing sentences in the box. (Điền lá thư giới thiệu với những câu thiếu trong khung.)
would like to recommend a well-known place in Vietnam to you.
It is about 170 kilometres from Hanoi.
The beach is an ideal place for swimmers.
People here are very friendly and hospitable.
I’m sure you will have a wonderful time here in Ha Long Bay.
Task 2: David, your pen pal, is going to spend his summer holiday in one of the ASEAN countries. You want him to visit Vietnam. Write a letter to him recommending a significant place you are familiar with. Use the outline below. (David, một bạn tâm thư của em, định trải qua kì nghỉ hè của anh ở một trong những quốc gia ASEAN. Em mùốn anh ấy thăm Việt Nam. Viết lá thư giới thiệu một nơi thú vị em biết. Dùng dàn bài bên dưới.)
20 Le Lai Street
District 1, HCM City, Vietnam
June 20th, 201...
Dear David,
I’m glad to hear that you’ve decided to spend your summer holiday in one of the ASEAN countries. So, I’d like to recommend you a wonderful place in Vietnam to you. It’s Hue, our ancient capital in the Central.
Hue was the capital of Vietnam during the Nguyen Dynasty and is one of the cultural cores of our country. The city lies on both sides of the Huong River (the Perfume River). In this ancient city can you find the palaces, pagodas and houses built on the same principles as the Forbidden Palace in Peking. Hue is also famous for its royal tombs, the tombs of the former emperors. It has been said these tombs are Hue’s most spectacular tourist attractions. And another fantastic attraction to tourists is the boat trip on the Huong River, especially on the moonlit nights. You can spend and enjoy the quiet and peace of the night time on the boat listening to the poetic songs of Hue’s singers. Besides these, you can also enjoy the quiet and poetic atmosphere of the garden houses of ancient architecture. Coming to Hue, you should not ignore to enjoy Hue’s specialties such “hen” rice, banh xeo (rice pancake with shrimps and herbs).
People in this old royal capital are said to be friendly and hospitable
I think you should come and visit it. I’m looking forward to hearing from you, and don’t forget to send my regards to your parents.
Best wishes,
Tam Le Minh
E. LANGUAGE FOCUS
Intonation: The rising-falling tune
Grammar: Adverbial clauses of time
♦♦♦ Grammar
Exercise 1: Complete each of the following sentences, using a suitable adverbial clause of time in the box. Use each clause once only. (Điền mỗi câu sau, dùng mệnh đề trạng từ chỉ thời gian thích hợp trong khung. Dùng mỗi mệnh đề chỉ một lần.)
She’ll phone you as soon as she arrives in Ho Chi Minh City.
After the war was over, we started rebuilding the country.
They met a lot of people while they were on holiday.
Before you leave, don’t forget to turn off the lights.
I’ll stay till you get back.
We’ll come to see you whenever we are in Hanoi.
There is a ganger of war as long as imperialism exists.
Tom sang a merry song as he walked / was walking away.
Exercise 2: Supply the correct tense form of the verbs in brackets.
(Cho dạng thì đúng của động từ trong ngoặc.')
arrives
arrives
are playing
got
have finished
had graduated
am
have read
Exercise 3: Combine two sentences, using one as an adverbial clause of time with the given conjunction.
(Kết hợp hai câu, dùng một câu như mệnh đề chỉ thời gian với liên từ được cho.)
Let’s go out before it starts raining/to rain .
I’ll give you my address when I have found somewhere to live.
After he had done his homework, he went to bed.
We’ll let you know as soon as we have made our decision.
haven’t met them since I left school.
Robert suddenly began to feel ill while he was doing the examination.
Kate will come back home after she has finished the last semester.