Giải tiếng Anh lớp 10 Unit 16: Historical Places
HISTORICAL PLACES
(Những nơi lịch sử)
I. VOCABULARY
site [salt]
originally [a’rnljanli] dynasty [‘dinasti] representative [repiT zentativ]
represent [repn’zent] representation [reprizen’teijn] representable [repn’zentabl]
Confucius [kan’fjujas]
(n) : vi tri
(adv): at first: đầu tiên, trước tiên (n) : triều đại
(adj) : tượng trưng, tiêu biểu (n) : đại diện
(v) : tiêu biểu, tượng trưng cho (n) : sự tiêu biểu/tượng trưng (adj) : có thể tiêu biểu (n) : Khổng Tử
Confucian [kan’fju:Jh]
(adj): thuộc Khổng giáo/Nho giáo
behaviour [bi’heivie]
(n) : hành vi
thought [eo:t]
(n): tư tưởng
thoughtful [‘eo:tfl]
(adj) : trầm tư
thoughtless [‘©o:tlis]
(adj) : không suy nghĩ
memorialize [me’mo:rialaiz]
(v) : tôn vinh, tưởng nhớ
scholar [‘skDle]
(n) : học giả
royal [‘roiel]
(adj) : thuộc về hoàng tộc
royal examination
(n) : thi Đình
engrave [in’greiv]
(v) : khắc, chạm trổ
engravement [in’greivment]
(n): sự chạm trổ, khắc
stele [lsti:li]
(n): tấm bia; stelea [‘stidi:] (sn)
giant [‘cfccuent ]
(adj): huge: khổng lồ
tortoise [lto:tas]
(n) : rùa (cạn)
well - preserved
(adj): được bảo tồn/gìn giữ kỹ
feudal [lfju:dl]
(adj): (thuộc) phong kiến
flourish [‘flAriJ ]
(v) : phát triển, thịnh vượng
initially [I’nijili]
(adv) : originally, at first: đầu tiên
ignore [ig’no:]
(v) : lờ đi
ignorance[ ig’no:rans]
(n) : sự ngu dốt/không biết
ignorant [ig’no:rant]
(adj): ngu dốt
ignorable [ig’no:rabl]
(adj) : có thể lờ đi
honor [lo:na]
(n) : danh dự, sự kính trọng (v) : tôn kính, kính trọng
honorable [‘omarabl]
(adj): đáng tôn kính/kính trọng
fall off [fo:l Df]
(v) : thoái hóa, suy đồi
take place
(v): happen, occur: xảy ra
function [‘fAQkfn]
(n) : chức năng
mausoleum [mo:sa’li:am]
(n):lăng
stand [staand]
(n): vị trí, khán đài
maintenance [‘meintanans ]
(n) : sự bảo trì, tu bổ
maintain [mein’tein]
(v) : duy trì, bảo quản
maintainable [mein’teinabl]
(adj) : có thể bảo quản
imperial [im’perial]
(adj) : thuộc về đế quốc
imperial city
(n): hoàng cung, kinh thành
heritage [‘heriticfc]
(n): di sản
citadel [‘sitadal]
(n):thành lũy
Royal Citadel [‘roial ‘sitadal]
(n): Thành nội
enclosure [in’klaơ3a ]
(n) : hàng rào vây quanh
Forbidden City [fa’bidn siti]
(n) : Tử Câm thành
admission fee [ad’mijn fi:]
(n) : lệ phí vào cửa
reunification [rijumifi’keijn]
(n) : thông nhất
reunify [n’jumifai]
(v) : thông nhất
bombardment [bDm’ba:dmant]
(n) : sự ném/dội bom
bombard [bDm’ba:d]
(v) : ném/dội bom
chamber [‘tfasmba]
(n) : phòng lớn
carve [ka:v]
(v) : khắc, chạm
merchant [lm3:tfant]
(n) : thương gia
pillar [‘pila]
(n) : cột, trụ
ornament [lo:namant]
(n) : vật trang hoàng, đồ trang sức
ornamental [oma’mentl]
(adj) : để trang trí
vessel f‘vesl]
(n) : thuyền/tàu lớn
certify [‘S3:tifai]
(v) : chứng nhận/thực
cerification [S3:tifi’keifn]
(n) : giấy chứng nhận
assembly [a’sembli]
(n) : cuộc họp, hội đồng
assembly hall
(n) : hội quán
congregation [kDr)gri’geifn]
(n) : sự hội họp, cộng đoàn
covered bridge [‘kywad brnfc
(n) : cầu Nhật Bản, cầu có mái che
trading centre [‘ treidir) senta]
(n) : trung tâm thương mại
Far East [‘fa:ri:st]
(n) : Viễn Đông
tile [tail]
(n) : ngói
tile-roofed
(adj) : mái lợp ngói
Cantonese Chinese [‘kaentani:z tjainkz] (n) : người Hoa ở Quảng Động
role [raul]
(n) : vai trò
arrival [a’raivl]
(n) : sự đến
tourist attraction [‘tuarist atraskjn]
(n) : điểm du lịch
(n) : ảo tưởng (n) : sự xoa bóp (n) : biện pháp
illusion [i’lu:3n ] massage [‘maesnfc] measure [‘me39]
IL GRAMMAR
A. COMPARATIVES and SUPERLATIVES {Dạng so sánh tương đối và tuyệt đối)
COMPARATIVES (Dạng so sánh tương đổỉ): được dùng so sánh giữa HAI sự việc hay HAI người,...
* Superiority (Bậc hơn)
- Adjectives and adverbs (Tính từ và trạng từ)
a. Short adjectives or adverbs (Tính từ/trạng từ ngắn): tính từ hay trạng từ có một vần, như: fast, late, high,...
s + V + adjective/adverb - ER + than + N.
e.g.: He’s taller than his brother.
{Anh ấy cao lớn hơn anh của anh ấy.)
He runs faster than me.
(Ân/z ấy chạy nhanh hơn tôi.)
b. Long adjectives or adverbs (Tính từ/trạng từ dài ): tính từ hay trạng từ có hai vần hay hơn hai vần, như: famous, careful, carefully,...
s + V + more + adj/adv + than + N.
e.g. : This city is more beautiful than my home town.
{Thành phố này dẹp hơn thành phố quê tôi.)
He works more carefully than this man.
{Anh ấy làm việc cẩn thận hơn người đàn ông này.)
* Chú ý: Tính từ HAI vần tận cùng bằng: -OW, -LE, -ER và -ET áp
dụng qui tắc tính từ ngắn.
g.: This test is easier than the last one. (easy)
{Bài tập này dễ hơn bài tập vừa qua.)
She’s cleverer than her sister, (clever)
{Cô ấy khéo tay hơn chị cô ấy.)
- Nouns (Danh từ)
s + V + more + N + than + N.
e.g.: My friend does more exercises than me.
{Bạn tôi làm nhiều bài tập hơn tôi.)
Viet earns more money than Nam.
{Việt kiếm nhiều tiền hơn Nam.)
* Inferiority (Bậc kém)
Adjectives and adverbs. (Tính từ và trạng từ)
s + V + less + adj/adv + than + N. e.g.: Hoa is less attentive than Nga.
{Hoa ít chăm chỉ hơn Nga.)
He works less fast than his workmate.
{Anh ấy làm việc ít nhanh hơn bạn đồng nghiệp của anh.)
Nouns (Danh từ)
Count nouns (Danh từ đếm được)
s + V + fewer + Ns + than + N.
e.g.: Mr Tan has fewer children than Mr Minh.
{Ong Tăn có ít con hơn ông Minh.)
Non-count nouns {Danh từ không đếm được)
s + V + less + N + than + N
e.g.: I have less free time than my friend.
{Tôi có ít giờ rảnh lum bạn tôi.)
SUPERLATIVES (Dạng so sánh tuyệt đối): được dùng so sánh giữa một với nhiều người/sự việc,... nghĩa là HƠN HAI người/sự việc,...
* Superiority (Bậc hơn)
- Adjectives and adverbs (Tính từ và trạng từ). a. Short adjectives/adverbs (Tính từ/trạng từ ngắn), s + V + the + adj/adv -EST.
e.g.: John is the tallest in my class.
{John là người cao lớn nhất trong lớp tôi.)
This athlete runs the fastest of all.
{Vận động viên này chạy nhanh nhất hơn tất cả.)
b. Long adjectives/adverbs (Tính từ/trạng từ dài)
s + V + the most + adj/adv.
e.g.: His son is the most intelligent student in school.
(Cơn trai anh ấy thông minh nhất trong trường.)
That driver drives the most carefully.
{Người tài xế kia lái xe cẩn thận nhất.)
Chú ý: Tính từ HAI VAN tận cùng bằng -Y, -OW, -ER, -LE và -ET được áp dụng qui tắc tính từ ngắn.
e.g. : This road is the narrowest in the region.
{Con đường này hẹp nhất trong vùng.)
Nouns (Danh từ)
s + V + the most + N . e.g.: My friend does the most exercises.
{Bạn tôi làm nhiều bài tập nhất.)
This district produces the most rice in the country.
{Huyện này sản xuất nhiều lúa nhất trong nước.)
* Inferiority (Bậc kém)
Adjectives/adverbs (Tính từ/trạng từ)
e.g.: The last test was the least difficult.
{Bài thi vừa qua ít khó nhất.)
This Street is the least noisy in the town.
{Con đường này ít ồn ào nhất trong thành phố.)
Nouns (Danh từ)
- Count nouns (Danh từ đếm được)
s + V + the fewest + Ns.
e.g.: Bill made the fewest mistakes in the test.
{Billphạm ít lỗi nhất trong bài kiểm tra.)
Non-count nouns (Danh từ không đếm được)
s + V + the least + N.
e.g.: This room has the least furniture.
{Căn phòng này có ít đồ đạc nhất.)
B. Pronouns after THAN (Đại từ sau THAN)
ở văn phong giao tiếp (informal style), đại từ túc từ (objective pronouns) thường được dùng.
e.g.: My friend is more intelligent than me.
{Bạn tôi thông minh hơn tôi.)
ở văn phong trang trọng (formal style), đại từ chủ từ được dùng, và được theo sau bởi động từ.
e.g.: You are more careful than we are.
{Bạn cẩn thận hơn chúng tôi.)
He speaks English more fluently than his brother does.
{Anh ấy nói tiếng Anh lưu loát hơn anh của anh ấy.)
c. MUCH, FAR, A LOT,... with comparatives (MUCH, FAR, A LOT,... với so sánh tương đối)
Chúng ta không dùng VERY với so sánh tương đối. Thay vào đó, chúng ta dùng MUCH, FAR, A LOT, ANY, LITTLE, A LITTLE,...
e.g.: He is much thinner than you.
{Anh ấy ốm hơn bạn nhiều.)
This bike is a little more expensive than mine.
{Chiếc xe đạp này hơi đắt tiền hơn xe đạp của tôi một ít.)
Chú ý: Chúng ta chỉ so sánh hai đôi tượng cùng chủng loại.
Chúng ta không nói: Compare your note with your partner.
- “your note” (sự việc): không thể so sánh với partner (người)
Nhưng phải nói: Compare your note with your partner’s (note).
III. SOLUTIONS and TRANSLATIONS {Lời giải và Bài dịch)
A. READING {Đọc)
BEFORE YOU READ {Trước khi em đọc)
Work in pairs.
List some historical places you know in Vienam. {Liệt kê một vài địa danh lịch sử ở Việt Nam).
-1 know some historical places like Den Hung Remains (Di tích đền Hùng), Dien Bien Phu, Cu Chi Tunnel (Địa đạo củ Chi), Hue Imperial City (Kinh thành Huế), Co Loa Citadel,...
Is Van Mieu - Quoc Tu Giam - a historical place?
- Yes, it is.
* Van Mieu is the largest and the most important temple in Ha Noi. It was founded in 1070 by Emperor Ly Thanh Tong, and dedicated to Confucius. In the Courtyard of the Stelea you can see 82 stelea, on which the names of successful examination scholars are recorded. Each stele is carried on the back of a tortoise, but ±ey are arranged in a chronological order.
WHILE YOU READ (Trong lúc em đọc)
Read the passage, and then do the tasks that follow. (Đọc doạn văn, và sau đó làm bài tập theo sau.)
Văn Miếu - Quốc Tử Giám - là địa danh văn hóa lịch sử nổi tiếng ở Hà Nội. Đầu tiên được xây năm 1070 vào triều đại nhà Lý, Văn Miếu tượng trưng cho phương cách suy nghĩ và hành xử theo Nho giáo. Sáu năm sau, Quốc Tử Giám, đại học đầu tiên ở Việt Nam, được thành lập trên nền tảng của Vãn Miếu. Khoảng giữa những năm 1076 và 1779, Quốc Tử Giám đã giáo dục hàng ngàn người tài ba cho đâì nuớc. Năm 1842, Văn Miếu trở thành nơi tôn vinh những học giả lỗi lạc của dân tộc. Tên, năm sinh và những thành tựu của những thí siijh đỗ đầu trong những kỳ thi Đình được khắc vào bia đá. Những bia đá này, đứng trên lưng những con rùa khổng lồ, ngày nay vẫn còn và chúng thu hút sự chú ý của khách thăm.
Sau hơn 900 năm hiện hữu, Văn Miếu là mẫu kiến trúc truyền thông Việt Nam được bảo quản kỹ lưỡng. Cây đa ở Văn Miếu, chứng kiến bao lễ hội và kỳ thi trong suốt những triều đại phong kiến tiếp tục phát hiển. Văn Miếu - Quốc Tử Giám - là một địa danh của niềm tự hào dân tộc của người dân Việt.
Task 1: Choose A, B, or c that best suits the meaning of the italicised word. (Chọn A, B, hoặc c phù hợp nhất với nghĩa của từ ìn nghiêng.)
B 2. A 3.C 4. B 5.C
Task 2: Decide whether the following sntences are True (T) or False (F). (Quyết định những câu sau đúng (T) hay sai (F).)
F (The construction of Van Mieu took place in 1070.)
T
F (Thousands of talented men were trained in Quoc Tu Giam from the 11* to the 18,h centuries.)
F (Van Mieu is still an example of well-preserved traditional Vietnamese architecture.)
T 6.T
AFTER YOU READ {Sau khi em đọc)
Work in groups. Talk about Van Mieu - Quoc Tu Giam, using the suggestions below. {Làm việc từng nhóm. Nói về Văn Miếu - Quốc Tử Giám, dùng những gợi ý dưới đây.)
Van Mieu - Quoc Tu Giam is a place of interest because it is a famous historical and cultural site in Hanoi.
They were built in Ha Noi by King Ly Thanh Tong in 1070 and in 1076.
Between 1076 and 1779, Quoc Tu Giam was a place to produce the talented for the nation. And 1482, Van Mieu became a place to memorialize the most brilliant scholars of the nation, who were successful students in royal examinations.
On the stone stelea, standing on the backs of giant tortoises, were engraved the names, places of birth and achievements of top students in royal examinations.
B. SPEAKING {Nói)
Task 1: A foreign visitor has taken some notes about President Ho Chi Minh’s Mausoleum. Ask and answer questions with a partner, using his notes. {Một khách ngoại quốc ghi chú về Lăng Chủ tịch Hồ Chí Minh. Hỏi và trả lời với một bạn cùng học. Dùng những ghi chú của ông ấy.)
A: Where is President Ho Chi Minh Mausoleum situated?
B: It is situated in Ba Dinh Square, in the centre of Ha Noi.
A: When did the construction of the Mausoleum started?
B: It started in 1973'and completed in 1975.
A: How many floors does it have?
B: It has three floors.
A: What are these floors used for?
B: Well, the first floor is used as a stand for important meetings organized at Ba Dinh Square. The second floor is the place where the late president is lying, and the third floor is the roof of the mausoleum.
A: On what days can you visit the Mausoleum?
B: In summer, you can visit the Mausoleum from 7:30 to 10:30 a.m. and in winter, you can visit it from 8:00 to 11:00 a.m., every day except Monday and Friday.
A: Can we take photographs?
B: You can take photos outside the Mausoleum, but inside you mustn’t.
Task 2: Work in pairs. Take turns to act as a tourist guide and give a short introduction to either of the historical places below, using the information given. {Làm việc từng đôi. Thay phiên đóng vai một hướng dẫn viên du lịch và cho lời giới thiệu ngắn về một trong những dịa danh lịch sử dưới đây, dùng thông tin
' được cho.)
HOÀNG THÀNH HUẾ
Được ghi vào danh sách Di Sản Văn Hóa Thế Giới năm 1993
Ở Huế, 654 km từ Hà Nội và 1071 km từ tp Hồ Chí Minh.
Xây dựng: khởi sự 1805 và hoàn tất năm 1832.
Bao gồm 3 khu vực: Hoàng Thành, Phòng Thành và Tử cấm Thành
Mở cửa mỗi ngày từ 8 giờ sáng đến 4:30 chiều.
Phí vào cửa: 55.000 đồng VN
HỘI TRƯỜNG THỐNG NHẤT
Cũng được gọi là Dinh Thông Nhất hay Dinh Độc Lập
Ở quận 1, tp Hồ Chí Minh, 1.730 km nam Hà Nội
Đầu tiên được xây năm 1865, và bị hư hại nặng trong vụ dội bom vào tháng Hai, 1963
Tái thiết và việc xây dựng hoàn tất năm 1966
Có 5 tầng với 100 phòng và phòng lớn trang trí đẹp đẽ
Mở cửa mỗi ngày từ 7:30 đến 11 sáng và từ lg đến 4g chiều
Phí vào cửa: 10.000 đồng
I’d like to introduce you all some features about Hue Imperial City. Hue is in Central Vietnam. It is 654 km far from Ha Noi and 1071 km from Ho Chi Minh City, and you can also get there by plane, about 45 minutes from Tan Son Nhat Airport.
Hue was listed as a World Cultural Heritage by UNESCO in 1993. Hue was founded by the Nguyen Dynasty. The construction started in 1805 and completed in 1832. Hue comprises three sections: the Royal Citadel, the Imperial Enclosure and the Forbidden City.
The City is open daily from 8:00 a.m. to 4:30 p.m. and the admission fee is 55,000 VND per person.
I’d like to introduce you the Thong Nhat Conference Hall. It is located in District 1, Ho Chi Minh City. The Hall was originally built in 1865 by the French to be the resident of the French governor (toàn quyền). Then it was called the Presidential Palace (Dinh Tổng thống), later the Independence
Palace (Dinh Độc lập). In February 1963, the building was heavily damaged by an aữ bombardment. And it was rebuilt and the reconstruction completed in 1966. After 1975, the building was called the Reunification Hall or the Thong Nhat Conference Hall. It has five floors with 100 beautifully decorated rooms and chambers.
The Hall is open daily from 7:30 to 11:00 a.m. and from 1:00 to 4:00 p.m. The admission fee is 10,000 VND per person.
Task 3: Work in groups. Ask other members of the group questions about a historical place they have been to or known about, note down the main information, then report to the class what you have learnt about the place. {Làm 'việc từng nhóm. Hỏi những thấnh viên khác của nhóm những câu hỏi về một địa danh lịch sử họ đã đến hoặc biết, ghi chú những thông tin chính, và sau đó tường thuật cho lớp những gì em biết về nơi đó.)
c. LISTENING {Nghe)
BEFORE YOU LISTEN {Trước khi em nghe)
Work in pairs. Look at the pictures, then answer the following questions. {Làm việc từng đôi. Nhìn vào các hình, và sau đó trả lời các câu hỏi sau.)
1.
Picture 1: Basilica of Notre Dame of Saigon (Vương Cung Thánh Đường Đức Bà Saigon)
Picture 2: Ha Long Bay
Picture 3: The Hue Bridge (Cầu Thê Húc) in Ha Noi
Picture 4: Noon Gate (Ngọ Môn) in Hue Imperial City.
I’ve been to the Basilica of Notre Dame of Saigon many times.
I’d like to visit Ngo Mon most because it is the remains of our ancient traditional achitecture.
WHILE YOU LISTEN {Trong khi em nghe)
Task 1: Listen and choose A, B, or c that best completes the sentence. {Nghe và chọn A, B hoặc c điền đúng nhất câu.)
B 2. A 3.C 4.C 5. c
Task 2: Listen again and answer the following questions. {Nghe lại và trả lời các câu hỏi sau.)
It lies on the Thu Bon River, 30 km south of Da Nang.
It was known as a major trading centre in Southeast Asia between the 16th and 17th centuries.
Hoi An is now famous for its old temples, pagodas, small tiled-roof houses and narrow streets.
They were made of wood and theừ pillars were carved with ornamental designs.
It was built in 1855.
It was built nearly two centuries ago.
The house now looks almost exactly as it did in the early 19lh century.
It was in 1999.
TAPESCRIPT
The ancient town of Hoi An lies on the Thu Bon River, 30 km south of Da Nang, it was formerly a major trading centre in Southeast Asia between the 16th and 17th centuries. Hoi An was also an important port for Dutch, Portuguese, Italian, Chinese, Japanese and other merchant vessels from the Far East.
Hoi An is famous for its old temples, pagodas, small tile-roofed houses and narrow streets. All the houses were made of wood and their pillars were carved with ornamental designs.
One of the main attractions of Hoi An is the Japanese Covered Bridge, which was built in the 16th century and is still well-preserved. All visitors to Hoi An are recommended a visit to the Assembly Hall of Cantonese Chinese Congregation. This house was built in 1855, and still keeps many precious objects that belonged to the Chinese community of Hoi An. Another attractive address to tourists is Tan Ky House, which was constructed nearly two centuries ago as a house of a Vietnamese merchant. The house now looks almost exactly as it did in the early 19th century.
In recent years, Hoi An has become a popular tourist destination in Vietnam. In 1999, it was certified as a World Cultural Heritage Site.
AFTER YOU LISTEN (Sau khi em nghe)
Work in groups. Talk about the ancient town Hoi An, using the following cues. (Làm việc từng nhóm. Nói về phố cổ Hội An, dùng những từ gợi ý sau.)
Hoi An is an ancient town in Central Vietnam after our ancient capital city Hue. It lies on the Thu Bon River and it was the trading centre in Southeast Asia in the 16th and 17th centuries. At present Hoi An is still an attractive tourist destination with its characteristics such old temples, pagodas, small tile-roofed houses and narrow streets.
Its main attractions are old architecture such as the Japanese Covered Bridge, Assembly Hall of Cantonese Chinese Congregation and Tan Ky House.
And one more special feature is all the houses were made of wood and their pillars were carved with ornamental designs.
WRITING (Viết)
Describing a chart (Mô tả biểu đồ)
Task 1: The chart on the right presents some information about visitor arrivals in Vietnam from the USA, France and Australia in 2001 and 2002. Study the chart and answer the questions that follow. (Biểu đồ bên phải trình bày một số thông tin về những chuyên đến của khách thăm Việt Nam từ Mỹ, Pháp và úc trong năm 2001 và 2002. Nghiên cứu biểu đồ và sau đó trả lời câu hỏi.)
The USA
99,700 French visitors arrived in Vietnam in 2001.
It is Australia.
No, it isn’t.
It is France.
The number of American visitors to Vietnam in 2002 increased by 29,497 people in comparison with that in 2001.
Task 2: Based on the answers to the questions above, write a description of the chart provided in Task 1. (Căn cứ vào những câu trả lời trên, viết bài mô tả biểu đồ được cung cấp ở Bài tập 1.)
The chart shows the number of visitor arrivals to Vietnam from the USA, France and Australia in 2001 and 2002. The statistics were provided by Vietnam National Administration of Tourism. It is clear that the number of visitors to Vietnam from the USA, France and Australia in 2002 is higher than that in 2001. According to the chart, the USA has the highest number of visitors. France comes to the second and Australia has a little fewer visitors than France although the number of Australian visitors to Vietnam in 2002 increased.
LANGUAGE FOCUS
Pronunciation: [ 3 ] - [ Ị ]
Grammar and vocabulary: 7. Comparatives and superlatives
Making comparisons
Grammar and vocabulary
* Comparatives and superlatives
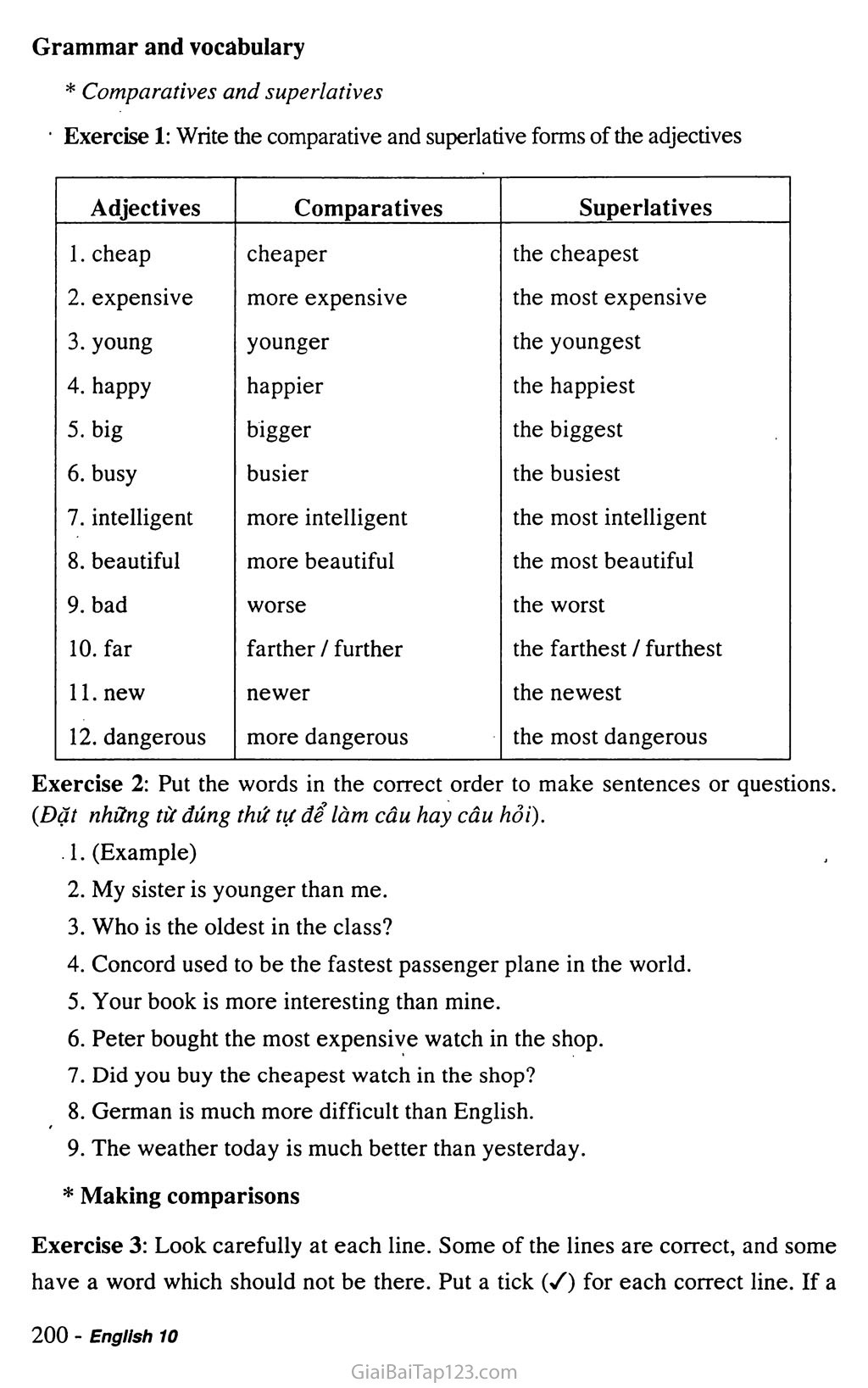
' Exercise 1: Write the comparative and superlative forms of the adjectives
Adjectives
Comparatives
Superlatives
1.cheap
cheaper
the cheapest
2. expensive
more expensive
the most expensive
3.young
younger
the youngest
4.happy
happier
the happiest
5. big
bigger
the biggest
6. busy
busier
the busiest
7. intelligent
more intelligent
the most intelligent
8. beautiful
more beautiful
the most beautiful
9. bad
worse
the worst
10. far
farther / further
the farthest / furthest
11. new
newer
the newest
12. dangerous
more dangerous
the most dangerous
Exercise 2: Put the words in the correct order to make sentences or questions. (£>ặ/ những từ đúng thứ tự để làm câu hay câu hỏi).
■ 1. (Example)
My sister is younger than me.
Who is the oldest in the class?
Concord used to be the fastest passenger plane in the world.
Your book is more interesting than mine.
Peter bought the most expensive watch in the shop.
Did you buy the cheapest watch in the shop?
German is much more difficult than English.
The weather today is much better than yesterday.
* Making comparisons
Exercise 3: Look carefully at each line. Some of the lines are correct, and some have a word which should not be there. Put a tick (•/) for each correct line. If a
line has a word which should not be there, write the word in the space. (Nhìn kỹ mỗi dòng. Một số dòng đúng, và một số có một từ đáng lẽ không nên đứng ở đó. Đặt dấu (S) cho mỗi dòng đúng. Nếu một dòng có một từ đáng lẽ không nên đứng ở đó, viết từ đó vào chỗ trống.)
Transport solutions (Những giải pháp chuyên chở)
- Line 1: farther
- Line 2: so
- Line 3: more
- Line 4: z
- Line 5: the
- Line 6: z
- Line 7: than
- Line 8: of
- Line 9: z
- Line 10: it
- Line 11: and
- Line 12: the
-Line 13: z
- Line 14: z
- Line 15: that